
Greater trochanteric bursitis, or more commonly known as "trochanteric bursitis" is an inflammation of a sac of fluid that covers the outside part of your hip.
Bursitis is often caused when the bursa becomes inflamed. The bursa is a small, jelly-like sac that often contains a small amount of fluid inside of it. These bursae are located throughout the body. The most important locations are the shoulder, knee, hip, elbow and heel. They serve as a cushion between the bones and all of the overlying soft tissues. They also work to help reduce friction between the bones and
the gliding muscles.
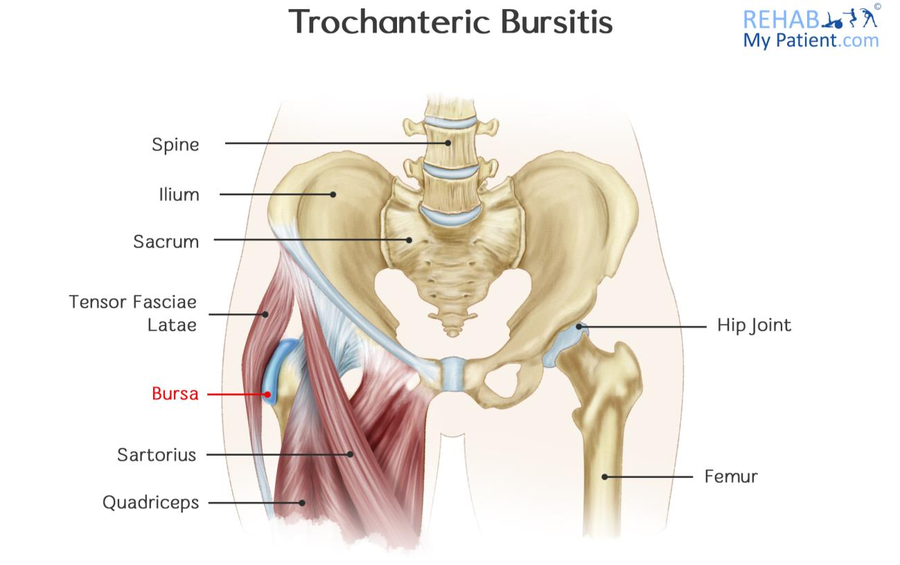
The bony part of the outside of the hip is known as the greater trochanter. It is an attachment point for the muscles responsible for moving the hip joint. The trochanter has relatively large bursa that lie over it, which can end up becoming irritated on occasion, resulting in what is known as bursitis.
Sometimes trochanteric bursitis can be difficult to diagnose, but in many cases the primary cause of the problem is a change in walking gait. So if you have been limping previously from a back problem, or knee problem, or a sprained ankle, that change in gait can change the biomechanics at the hip joint leading to a bursitis. Changes in shoes can also be a problem, especially for runners and long distance walkers. Other causes can be a wide-hip angle, hence women with a wider hip angle are more likely to get trochanteric bursitis. For the same reason, it's far more common in women than in men (as men tend to have a narrower pelvis).
Patients tend to report pain when lying on the affected side, especially in bed or if they have a hard mattress. Patients also report pain that radiates down the leg into the front and lateral part of the thigh, often to the knee joint.
Trochanteric Bursitis Anatomy
Bursitis is often responsible for pain on the side of the hip, which can make it difficult to lay on that side. The bursa has the job of protecting all of the other tissues from compression and friction. Too much stress, such as that of a direct blow can end up causing the bursa to become inflamed. The job of the bursa is to prevent any friction between the tissue known as the Iliotibial Band and the Greater Trochanter.
How to Treat Greater Trochanteric Bursitis:
- Rest
Rest is critical to the treatment of bursitis to allow the condition to settle down. You need to take time and allow the area ample time to relax and remain still. Avoid engaging in any activities that are going to worsen the condition or cause more inflammation to occur. - Physiotherapy or Manual Therapy Treatment
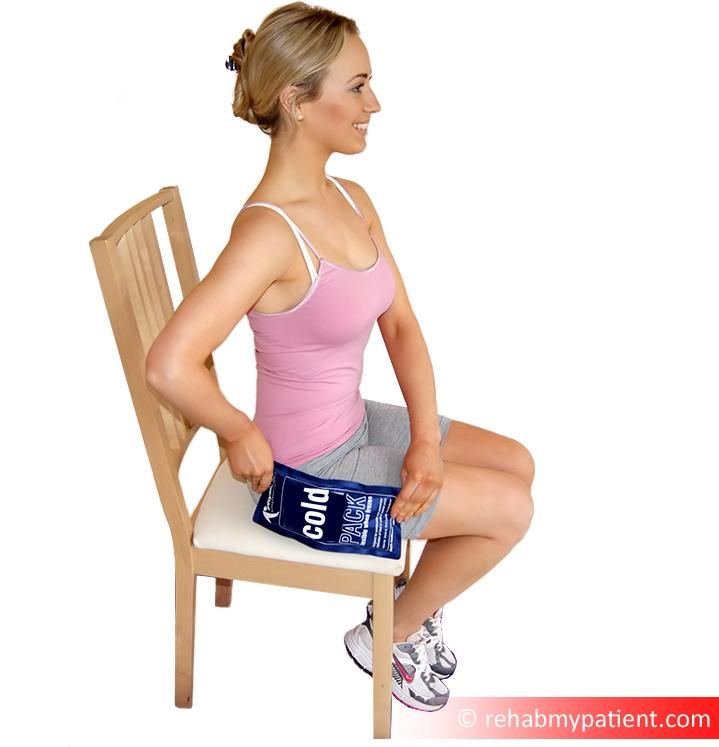
This type of treatment often includes ice therapy, stretching of the Ilio Tibial Band and electrotherapy. These techniques might be successful in being able to cure the condition. Ice packs should be applied for five to 10 minutes at a time three to five times per day. Avoid applying ice directly to the skin so as
to prevent an ice burn from occurring. Using ice will help to alleviate pain and inflammation in the area. - Corticosteroid Injections
In cases of long-term bursitis, it might be necessary to have these injections to help allow the condition time to settle down and alleviate any pain and inflammation in the area. Steroid injections in the area can be very successful as they hit the inflammation hard and can give sufferers quite a step forwards. But therapy should be followed up after an injection so that the underlying issues can be addressed. - Ice
Ice is incredibly important, and should be used over the area (the outside of the hip) for 4-6 weeks every day. Try to use the ice twice per day, and make sure you wrap it in a tea-towel so that you do not risk an ice-burn.

Tips:
- Avoid engaging in any activities that are going to place undue stress on your hips.
- Avoid sleeping on the side that hurts, if possible.
- Avoid over-hard mattresses, or look for soft topper mattresses that may offer some give and prevent pressure on the hip.
- If you are overweight, you might want to lose the extra weight to help take the pressure of the hips.
- Wearing shoes that fit properly is important.
- Maintain your flexibility and strength in the hip muscles.
- If you are a sportsperson, especially a runner or cyclist, make sure you use proper technique and good bike set-up. Ask the advice from a coach.
- Use caution when running, climbing stairs, standing for an extended period of time and cycling.
Zapisać się
Zarejestruj się już teraz, aby skorzystać z bezpłatnego okresu próbnego!
Zacznij korzystać z Rehab My Patient już dziś i zrewolucjonizuj proces przepisywania ćwiczeń, aby zapewnić sobie skuteczną rehabilitację.
Rozpocznij 14-dniowy bezpłatny okres próbny