Hip Adductor Strain
Opublikowano dnia 04th May 2017 / Opublikowano w: Biodro

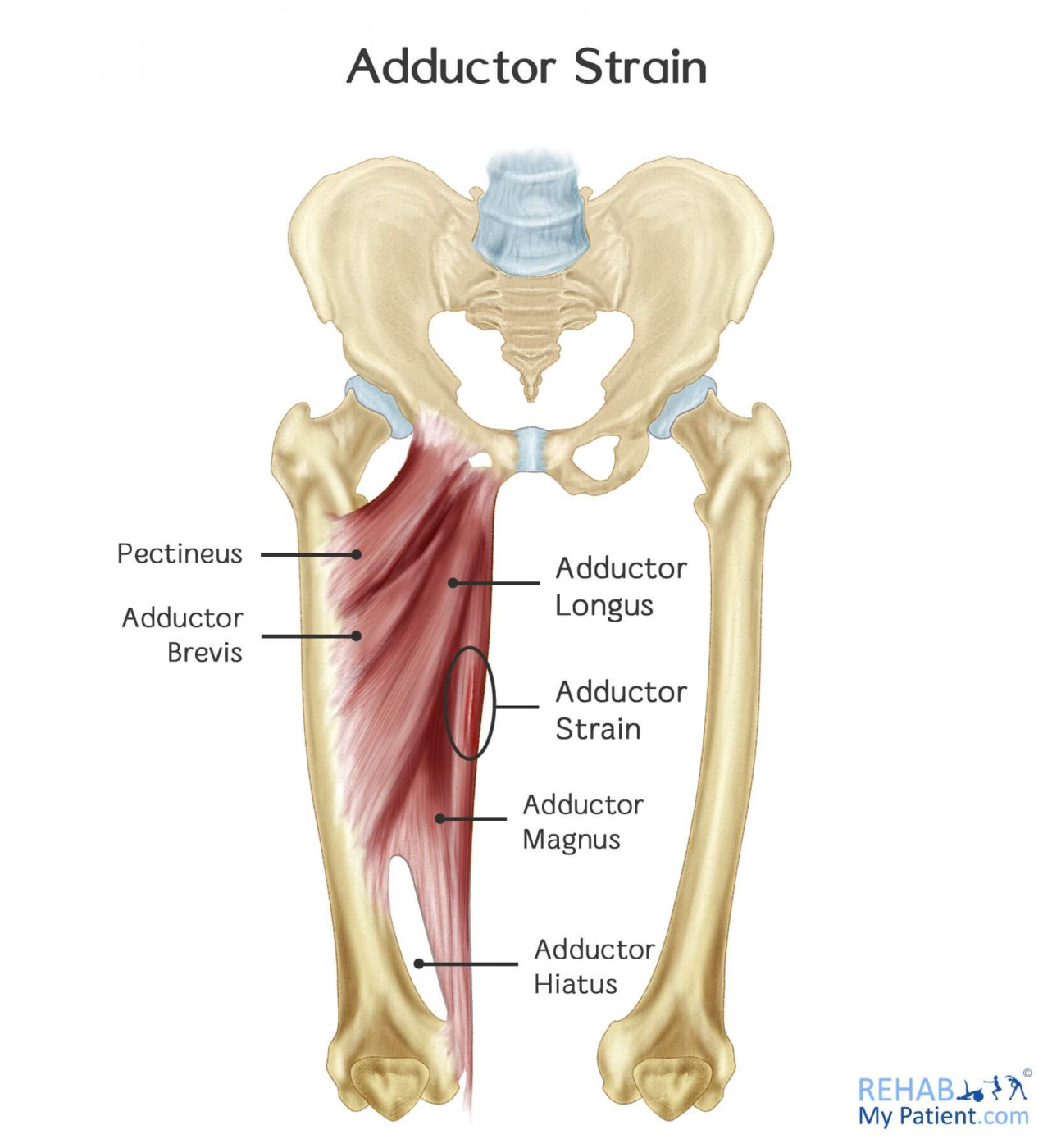
Hip adductor muscles are sometimes called your “groin” muscles, and a hip adductor strain can be called a groin strain. There are three muscles located on the inside of the leg.
Hip adductor strains tend to occur when the tendons or the muscles in the hip are stretched or torn during sports or exercises. Most of the time, these injuries will require multiple weeks of rest, medication and therapy to make sure the strain has healed completely before being able to return to any physical activity.
An adductor strain can be classified depending on its severity, grade I, II or III. Grade I tends to be a minor strain, and can cause pain for up to 4 weeks. Grade III’s are severe and can end a sports season, usually representing a full tear to the muscle or in severe cases a rupture.
Hip Adductor Strain Anatomy
The hip is a ball and socket joint connecting the thigh bone (femur) to the pelvis socket. It allows the leg to move. The hip joint is composed of multiple parts, including that of the lesser and greater trochanters. The greater trochanter is the place where countless muscles from the buttocks allow and meet to promote hip abduction and movement from one side to the other. When it comes to the lesser trochanter, this is the point where the iliopsoas muscle is attached to the hip joint to provide for forward movement within the leg, which is otherwise referred to as hip flexion.
How to Treat a Hip Adductor Strain:
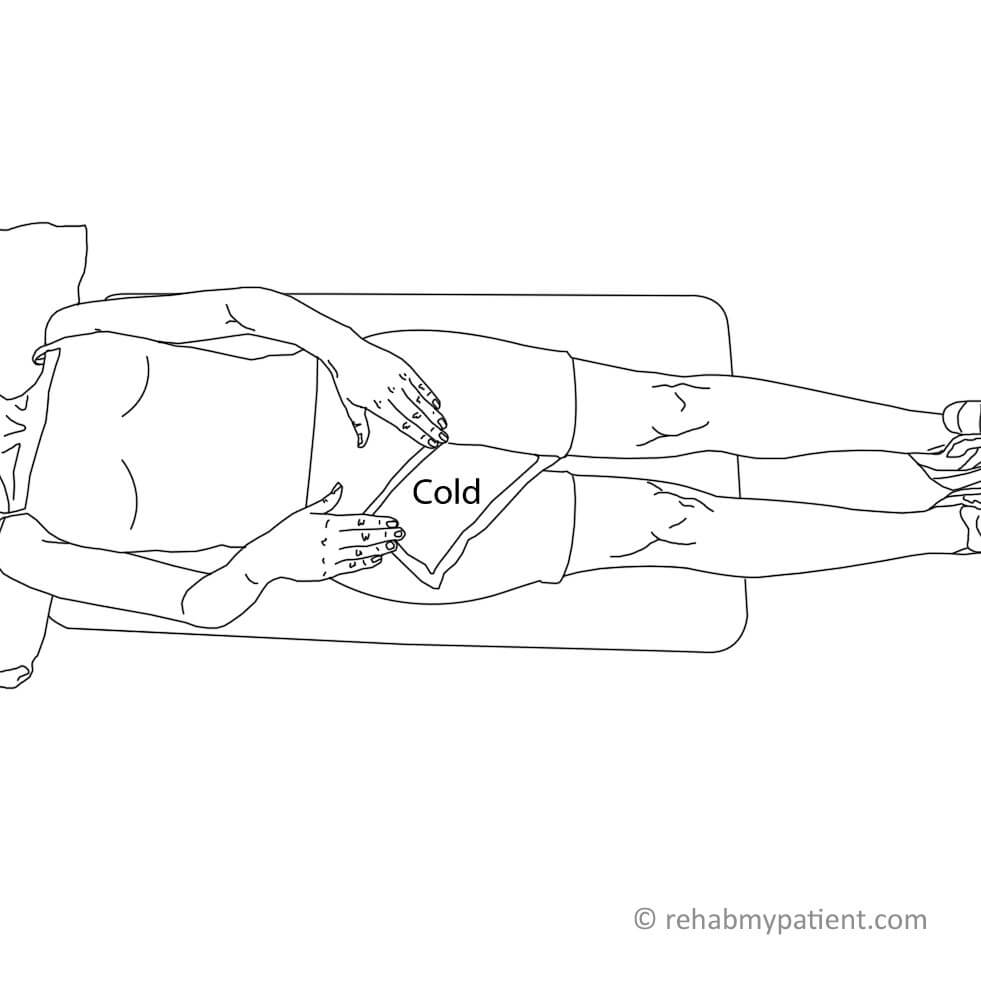
- Ice
Apply ice to the affected are for 5-10 minutes at a time, three to five times per day. Ice helps to reduce swelling and inflammation, which will help to minimize pain in the area.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medication
An anti-inflammatory medication will help to reduce inflammation in the affected joint. When you are able to reduce inflammation, it will help to decrease the amount of pain you are feeling in the area. Discuss with your therapist how long you should use it for, and if you should take it after food. Ice and/or heat might work just as well as medication.
- Rest
Resting the injured area, either by refraining from physical activity or changing to another activity that won’t affect the hip, such as swimming, is another component to aid in the healing process. Speak to your therapist about when you can return to sport.
- Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is great for rehabilitating the hip. Beyond helping to improve range of movement, it also helps to increase muscle strength and prevent undue injuries from occurring in the first place. Specific exercises will be provided to address your individual level of injury and pain. Electrotherapy may also be used to speed up tissue repair, such as ultrasound, LASER or TENS.
Make sure you receive the adequate therapy as groin strains can become chronic, causing months of misery. The problem tends to be worse the higher up into the groin, especially where the groin muscle attaches to the pelvis via a tendon.
Tips:
- Once the hip adductor has had the chance to heal, it is important that you try and prevent any future injuries from occurring. Improve strength and maintain flexibility to the hip adductors, hamstrings and quadriceps.
- Before beginning any activity, take the time to warm up to help minimize the risk of injury.
- Physical therapy can help strengthen the hip muscles and prevent any injuries from occurring.
- Since everyone heals at a different rate, you need to get clearance before you begin to regular activities.
- Before you begin to your normal activities, you should have regained full range of movement and be capable of sprinting, jogging and jumping on the injured leg without being in a great deal of pain.
- Be careful with hard stretching to the groin muscles. They are small and delicate and can be torn simply by over-stretching (as your author knows well!).
Zapisać się
Zarejestruj się już teraz, aby skorzystać z bezpłatnego okresu próbnego!
Zacznij korzystać z Rehab My Patient już dziś i zrewolucjonizuj proces przepisywania ćwiczeń, aby zapewnić sobie skuteczną rehabilitację.
Rozpocznij 14-dniowy bezpłatny okres próbny