Anterior Wedge Fracture to the Vertebra
Opublikowano dnia 08th Apr 2018 / Opublikowano w: Kręgosłup lędźwiowy , Odcinek piersiowy kręgosłupa

Anterior wedge fractures are fractures that occur when the vertebrae in the spine break down from some form of trauma. The fracture can also be caused by cancer, osteoporosis and any number of other conditions. Symptoms often include weakness and pain but can in rare cases cause nerve pains, tingling or incontinence.
By far the biggest contribution to wedge fractures is osteoporosis. If the spine is osteoporotic, there is thinning of the bone and even small traumas or falls might cause a collapse. Rarely, the collapse can occur without explanation, with the sufferer having no recollection of a fall or trauma.
In most cases, trauma has occurred and the majority of traumas involve a fall where person slips and lands on their backside. The fracture typically occurs at the level between the upper and lower back, known as the thoraco-lumbar junction. Common vertebrae affected are T11, T12, and L1.
Anterior wedge fractures are often called vertebral crush or vertebral compression fractures.
Many different tests can diagnose if you do indeed have one of these fractures.
Anterior Wedge Fracture Anatomy
Bones in the spine are known as vertebrae (plural). They are stacked one on top of each other and are joined by facet joints and discs that sit in-between each vertebra. Spinal nerves are at each level and exit from the spinal cord through holes between the vertebrae known as foramen.
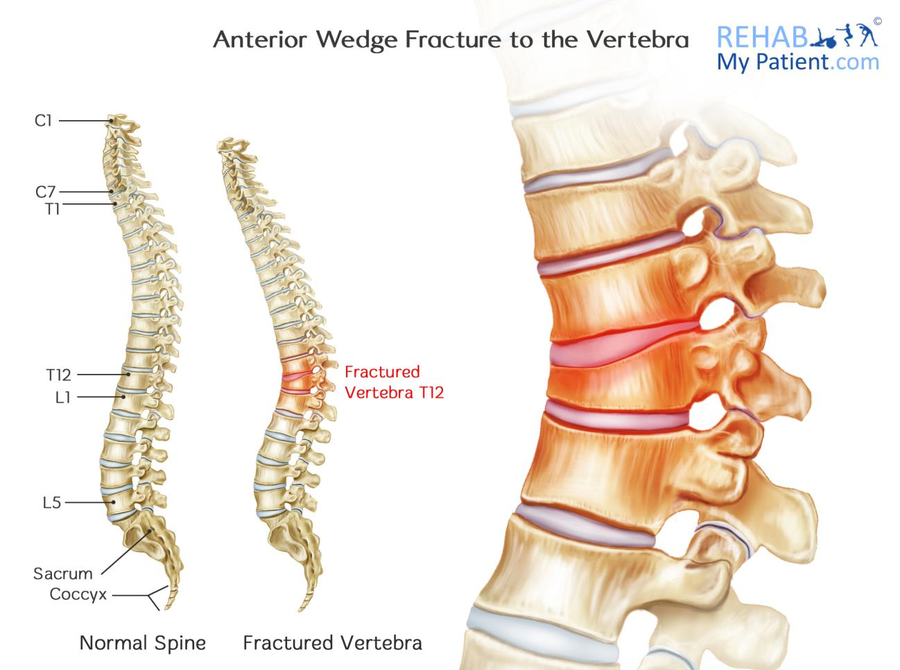
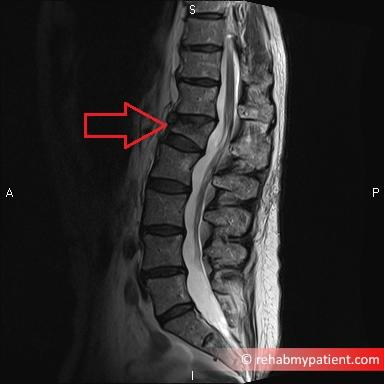
When the vertebra crushes or collapses, it tends to collapse at the front. This is why compression fractures are sometimes known as anterior wedge fractures. As the bone at the front of the vertebra collapses, it forms a wedge shape. Depending on the severity of the fracture will depend upon the level of wedging that occurs. Also if there is underlying weakness in the bone, for example in osteoporosis, then the wedging is likely to be more pronounced.
In a younger person without osteoporosis, the trauma would need to be significant to have enough force to fracture the vertebra.
How to Diagnose an Anterior Wedge Fracture to the Spine
Diagnosis is not easy and it’s possible for these to be missed. In some cases with just a history it is possible to diagnose the fracture, for example if a known osteoporotic person has had a fall. However, in many cases, the pain may present as other issues in the spine. During a physical examination there are some tests which can be done to help diagnose an anterior wedge fracture, however it is known that these tests are not particularly reliable and can create false-positives.
The ideal way to see a compression fracture is with an X-Ray or MRI scan. If the fracture is severe, then a CT scan may also be performed.
Problems Following an Anterior Wedge Fracture of the Spine
In the early days, there will be pain around the injury site. However, once this pain and restriction settles, patients often report pain lower down their spine at the base of the spine. This is because the wedging of the vertebra causes a forward shift of weight-bearing which places more strain in the lower back. Sometimes this can become very chronic and patients may have to deal or manage with a certain level of pain or discomfort at the base of the spine.
How to Anterior Wedge Fractures:
- Anti-Inflammatory Medication
An anti-inflammatory medication is often prescribed to help in terms of pain and inflammation. Medication won’t help the fracture heal, but it will help you to deal with the pain. This should be used short-term. - Kyphoplasty
If the fracture is deemed suitable for surgery, there is a surgical procedure known as kyphoplasty. It is a relatively minor procedure although it does require a general anaesthetic. A small balloon is placed into the vertebral body and inflated to create a cavity within the collapsed vertebrae. This is then filled with cement, after the balloon has been removed, leaving just the cement in the vertebra. The cement hardens within a few minutes stabilizing and potentially increasing height of the vertebra. - Modification of Activities
Activities that cause pain in the back should be avoided. Modifying your activities according to what your individual pain level and tolerance is can help to avoid additional injuries from occurring. The most important rule is absolutely no forward bending. This places too much stress on the front of the vertebrae. Also don’t try and lift anything heavy, or anything that is going to cause too much strain on the fractured site. Elderly individuals are often put on bed rest during this time. Older bones tent to be weaker and thinner, so they are going to take longer to heal. Treat the fracture seriously and carefully. - Bracing
Applying a brace to the affected area can help to prevent additional movement and pulling of the injured site. Braces can help to keep the spine securely in place to promote the healing process. Since it restricts movement in the spine and conforms tightly to your body, it will prevent you from bending over. The spine is held in a neutral position, which alleviates pressure on the fractured vertebrae and allows it to heal properly.
Tips:
- Osteoporosis is one of the common causes of compression fractures. Try to maintain bone health and a good nutritious balanced diet as much as you can. Make sure you get adequate amounts of calcium.
- Trauma to the spine can cause minor, if not severe, fractures.
- Cancer can cause the bones to be destroyed to the point where they collapse from being too weak.
- When lifting an item, make sure to lift with your legs and not with your back.
- Expect chronic pain or stiffness at the base of the spine following a wedge fracture.
Zapisać się
Zarejestruj się już teraz, aby skorzystać z bezpłatnego okresu próbnego!
Zacznij korzystać z Rehab My Patient już dziś i zrewolucjonizuj proces przepisywania ćwiczeń, aby zapewnić sobie skuteczną rehabilitację.
Rozpocznij 14-dniowy bezpłatny okres próbny