Infrahyoid
Opublikowano dnia 24th Jul 2020 / Opublikowano w: Szyja

General information
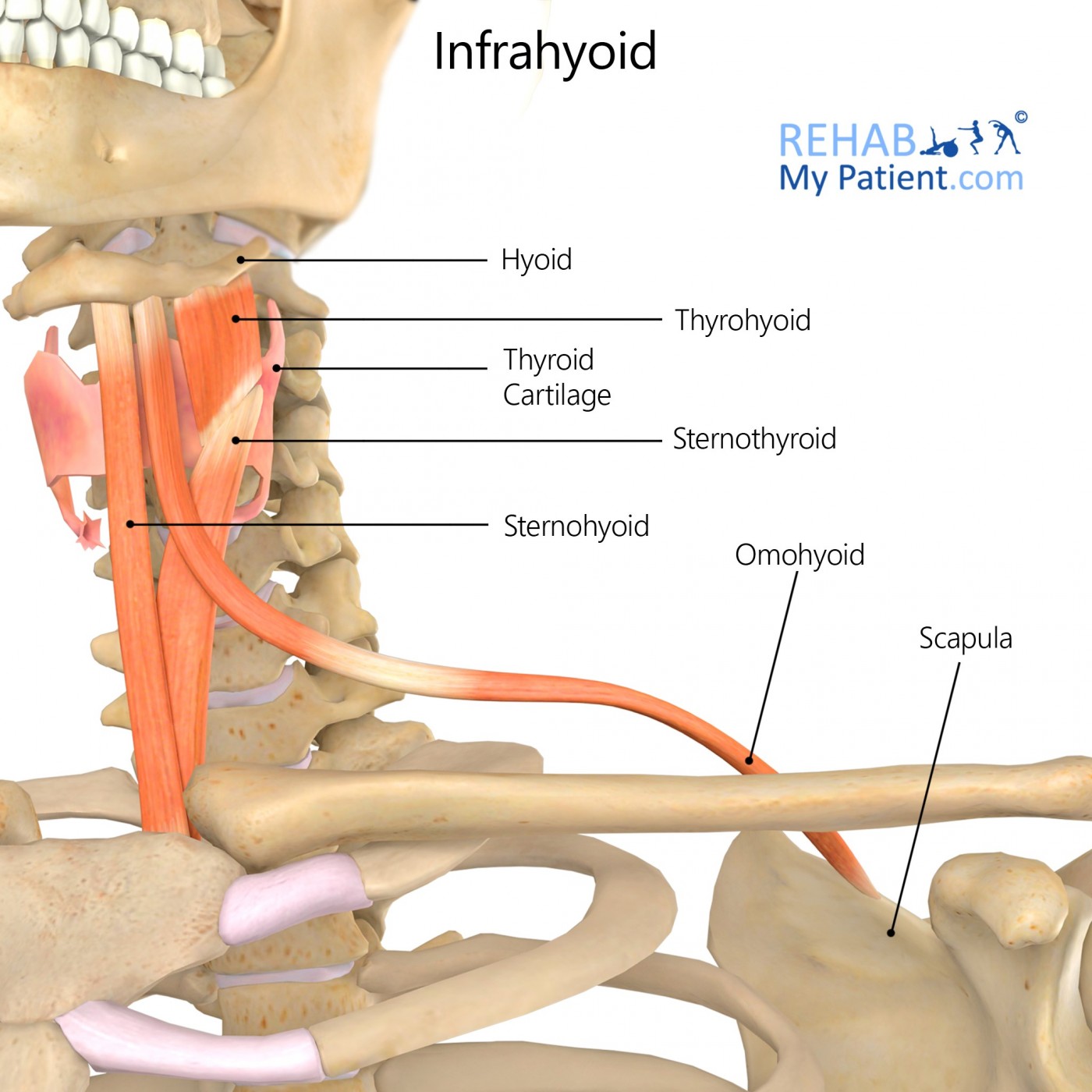
The infrahyoid muscle group is made up of four muscles, situated under the hyoid bone.
Literal meaning
Below the hyoid bone.
Interesting information
The Infrahyoid muscles can be divided into two groups:
Superficial plane – made up of the omohyoid and sternohyoid muscles
Deep plane – consisting of the sternothyroid and thyrohyoid muscles
The sternohyoid is the most superficial of the group.
Paralysis of the Infrahyoid muscles can occur when cervical spine trauma leads to ansa cervicalis damage. This can cause difficulties swallowing, a hoarse speaking voice and tightness in the throat.
Origin
Omohyoid muscle: The omohyoid muscle is divided into a superior and inferior belly. The inferior belly begins at the superior border of scapula.
Sternothyroid muscle: The dorsal surface of the manubrium
Thyrohyoid muscle: The oblique line of thyroid cartilage
Sternohyoid muscle: The dorsal surface of manubrium and the sternoclavicular joint and its insertion on.
Insertion
Omohyoid muscle: The body of hyoid.
Inferior belly- ascends craniomedially and merges into an intermediate tendon at the height of the lateral cervical region.
Sternothyroid muscle: The oblique line of thyroid cartilage.
Thyrohyoid muscle: The body of hyoid and greater cornu.
Sternohyoid muscle: The body of hyoid.
Function
The infrahyoid muscles: Depress the hyoid, except the sternothyroid; Position the hyoid bone; important in swallowing and the movement of the larynx.
Sternothyroid: depresses the larynx
Thyrohyoid: elevates larynx when hyoid bone is fixed
The omohyoid: Additional function; it maintains a low pressure in the internal jugular vein.
Nerve supply
All four infrahyoid muscles are supplied by the deep Ansa cervicalis (C1-C3), which arises from the cervical plexus.
The thyrohyoid receives additional supply through branches of the superior root of ansa cervicalis accompanied by the hypoglossal nerve.
Blood supply
The superior and inferior thyroid arteries.
Relevant research
A study involving the dissection of 35 male cadavers set out to investigate variations in the omohyoid. This is important because the omohyoid is the surgical landmark for identifying the location of the internal jugular vein. Variations in the omohyoid muscle may increase the risk of injury to the internal jugular vein during surgery. 85% (n. 30) of the cadavers were found to have standard attachment and position of the omohyoid. Of the remaining five, one was found to have a double omohyoid, with the others having different variations of size and attachments.
Rai, R., Ranade, A., Nayak, S., Vadgaonkar, R., Mangala, P., & Krishnamurthy, A. (2008). A study of anatomical variability of the omohyoid muscle and its clinical relevance. Clinics (Sao Paulo, Brazil), 63(4), 521–524. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1807-59322008000400018
Infrahyoid exercises
None specific to these muscles.
Zapisać się
Zarejestruj się już teraz, aby skorzystać z bezpłatnego okresu próbnego!
Zacznij korzystać z Rehab My Patient już dziś i zrewolucjonizuj proces przepisywania ćwiczeń, aby zapewnić sobie skuteczną rehabilitację.
Rozpocznij 14-dniowy bezpłatny okres próbny