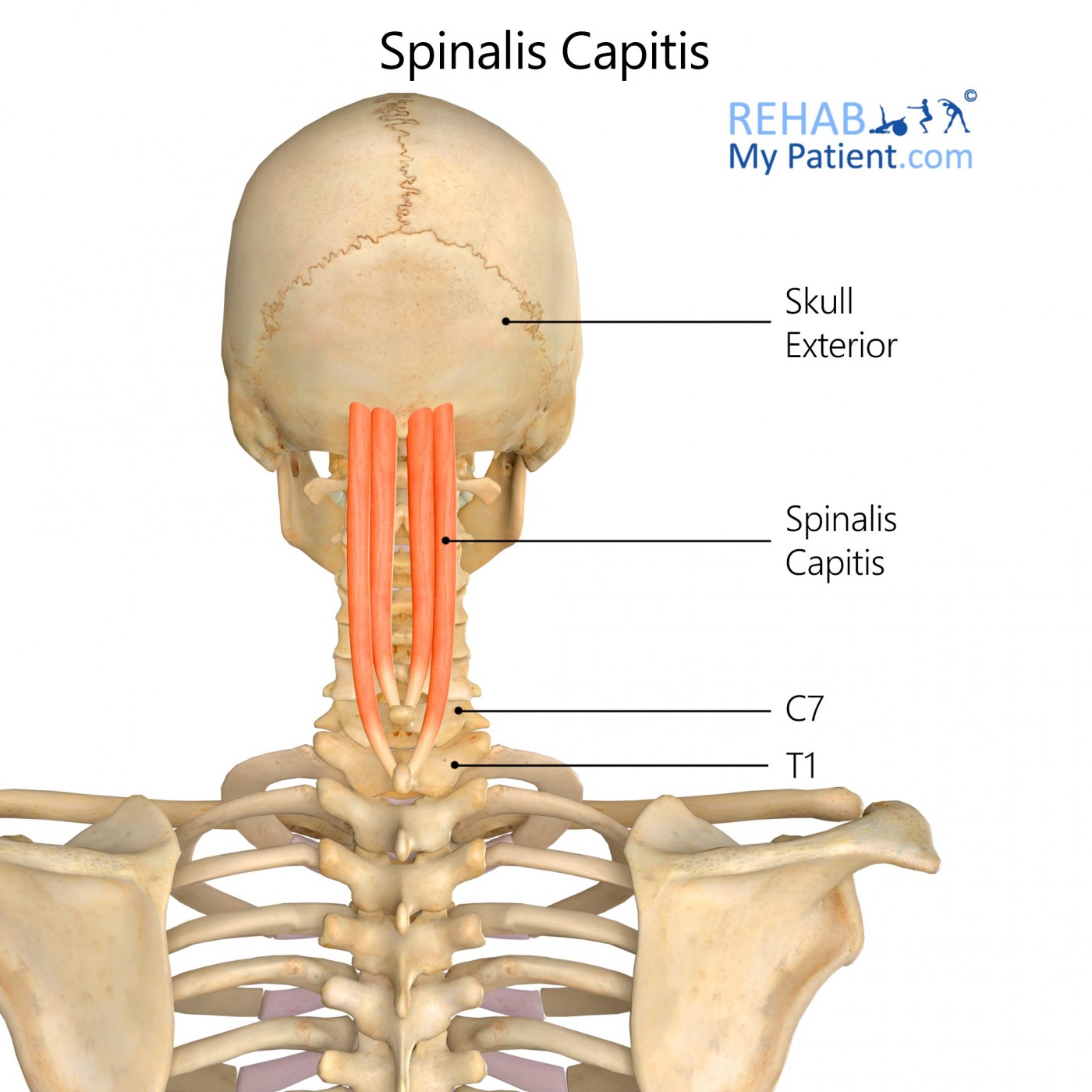
Spinalis Capitis
Opublikowano dnia 29th Jul 2020 / Opublikowano w: Szyja

General information
The Spinalis capitis is often connected with the Semispinalis capitis.
Literal meaning
Thorn head.
Interesting information
Common activities that cause pain in the Spinalis capitis are whiplash, cervical collar, stress, a blow to the back of the head and holding the shoulders up due to a lot of stress. If unsure about whether this muscle has been affected, look for a few of the telltale symptoms of a Spinalis capitis injury. Headaches, pain in the back of the upper portion of the neck that extends upwards to the back of the head, a band of pain that goes around the top portion of the head, pain radiating in the temple region and extending down to the eye, scalp numbness and a tenderness within the back of the neck and head are all symptoms of pain that are associated with an injury to the Spinalis capitis muscle.
Origin
Side of the Spinous process of C7.
Insertion
Near the midline located between the inferior and superior nuchal lines of the occipital bone.
Function
Aids in extending the vertebral column and the head.
Nerve supply
Dorsal rami in the cervical spine nerves C1-C3.
Blood supply
Muscular branches of the vertebral artery from the subclavian and muscular branches from the occipital artery from the external carotid artery.
Relevant research
The purpose of the evaluation was to demonstrate the appearance of the greater occipital nerve on the ultrasound. The occipital nerve was evaluated in 21 patients, of which nine were men and 12 were women with an average age of 52 and an average weight of 74.5 kilograms, at the time of the carotid duplex ultrasound. All of the examinations were performed by the same sonographer. To maintain consistency and uniformity, the sonographer used the same type of ultrasound unit for all the tests. The anatomical landmark that was used for locating the nerve was that of the inferior spinalis capitis muscle. The study found sonographic evidence that shows an increased cross-sectional area and circumference of the symptomatic greater occipital nerve in patients who have unilateral occipital neuralgia.
Cho JC, Haun DW, Kettner NW. Sonographic evaluation of the greater occipital nerve in unilateral occipital neuralgia. J Ultrasound Med. 2012; 31(1):37?42. doi:10.7863/jum.2012.31.1.37
Spinalis capitis exercises
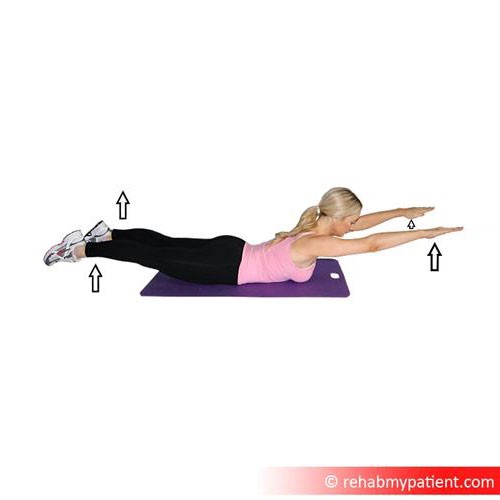
Superman
The superman move works to target the erector spinae muscles. Lie with the face down on a mat. Put the legs together and arms straight out in front of the body. Raise the upper body slowly and lift the legs off the floor as high as possible. Pause and return the upper body and legs to the floor for a complete rep. Complete 10 repetitions of the exercise.

Back extension
Lie face down on the exercise ball with the feet pressed flat against the wall base. Put the arms to the sides or clasp them behind the hips. Raise the torso off the ball by hyperextending the spine. Lift until the body forms a straight line from the shoulders to the knees. Return to start for one rep. Complete 10 repetitions of the exercise.
Zapisać się
Zarejestruj się już teraz, aby skorzystać z bezpłatnego okresu próbnego!
Zacznij korzystać z Rehab My Patient już dziś i zrewolucjonizuj proces przepisywania ćwiczeń, aby zapewnić sobie skuteczną rehabilitację.
Rozpocznij 14-dniowy bezpłatny okres próbny