Supraspinatus
Opublikowano dnia 29th Jul 2020 / Opublikowano w: Ramię

General information
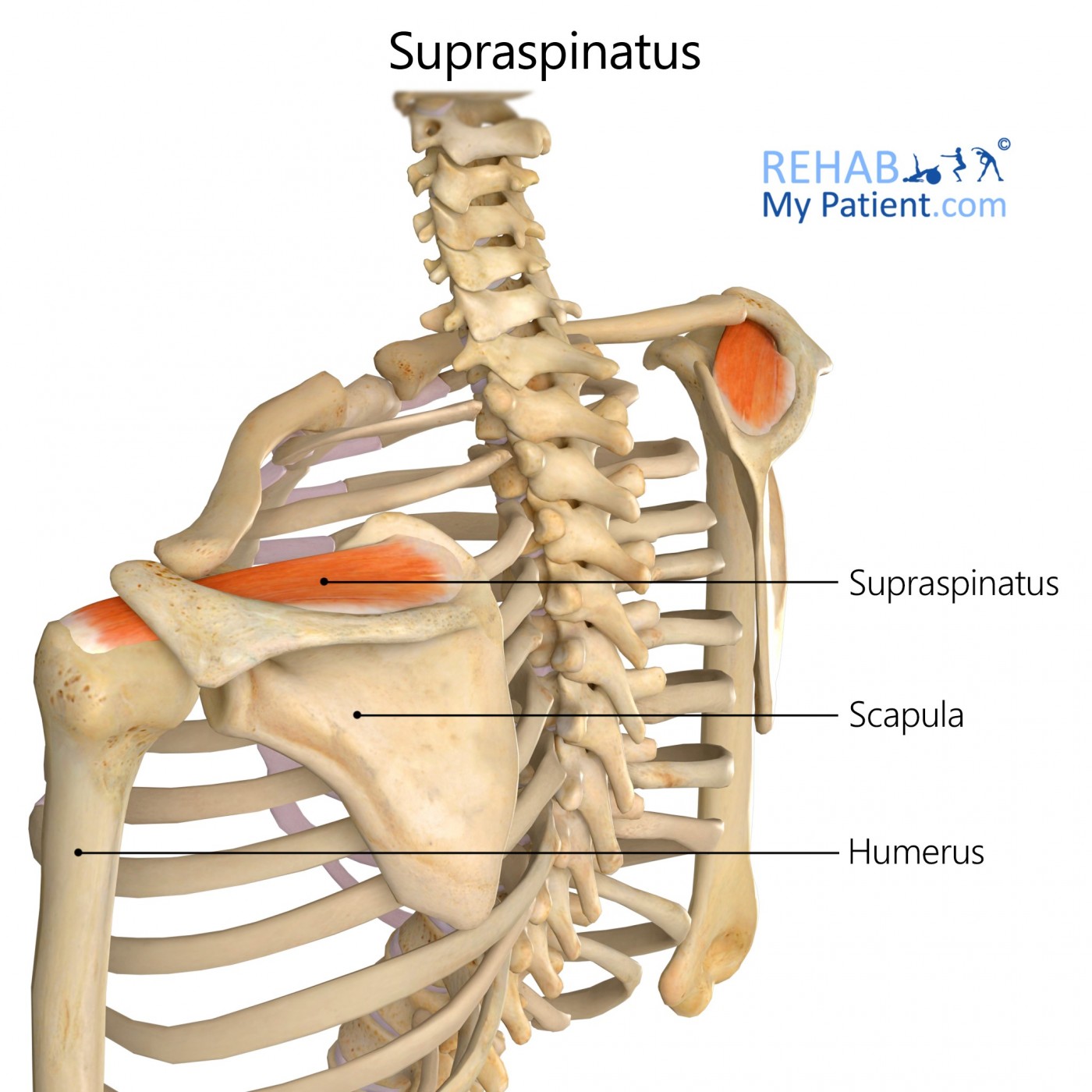
The supraspinatus muscle is one of the smaller muscles within the upper back running from the supraspinatus fossa superior in the scapula to the greater tubercle within the humerus. As one of the four rotator cuff muscles, it abducts the arm at the shoulder. The scapula’s spine separates this muscle from the infraspinatus muscle originating below the spine.
Literal meaning
Above or over thorn.
Interesting information
The supraspinatus muscle runs along the top of the shoulder blade and into the tendon located at the top of the arm. As one of the rotator cuff muscles, it is used to lift the arm upward to a sideways position. Contraction of the supraspinatus abducts the arm at the shoulder point and it is the main agonist muscle used in the first 15° of the arc, before the deltoid takes over. It is also widely used when participating in sports, especially when releasing an object being thrown. There are massive forces used to slow the arm down after throwing something, but not many people take the time to train the muscles adequately. Heavy falls on the shoulder can cause the muscle to become injured.
Over top of the tendon is the bursa, which is a small sac of fluid that is used for lubricating the moving tendon. It is possible for the bursa to become inflamed. Athletes tend to be more prone to this type of injury when overusing the shoulder, especially when the arm is at or above shoulder level. Those who have suffered with a ruptured supraspinatus tendon are more prone to injury as well.
Origin
Supraspinous fossa in the scapula and the overlying supraspinous fascia.
Insertion
Superior most aspect for the greater tubercle in the humerus.
Function
Abduction of the humerus.
Stabilization of the shoulder joint.
Nerve supply
Suprascapular nerve C5-C6.
Blood supply
Suprascapular artery.
Dorsal scapular artery.
Relevant research
Tears in the rotator cuff are one of the most common of all tendon disorders in healthy individuals. Changes that transpire in muscles after the tendon becomes detached are poorly understood. In this study, a rat rotator cuff muscle was used to help determine what the course of changes were in supraspinatus muscle after the tendon was detached. It was believed that the lack of load for the supraspinatus muscle can cause a substantial decrease in the muscle mass and conversion of fibers toward that of the fast fiber type. Results suggest that when the load returned to the muscle it may be significant enough to reverse the changes of the muscle mass.
Barton ER, Gimbel JA, Williams GR, Soslowsky LJ. Rat supraspinatus muscle atrophy after tendon detachment. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(2):259-265. doi:10.1016/j.orthres.2004.08.018.
Supraspinatus exercises
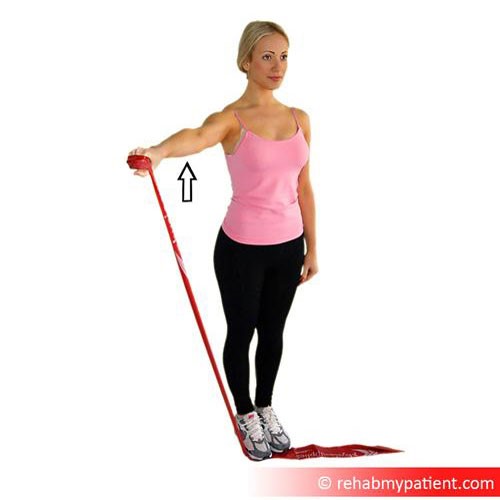

Single arm resistance band abduction
This particular exercise targets each supraspinatus individually. Using the right foot, anchor the middle of the resistance band to the floor. Hold both ends of the band in the right hand with the palm turned to the body. Lift the arm to shoulder level at 45-degrees in relation to the torso. Lower the right palm back to the thigh to complete one rep on the right side. Perform the same exercise on the left side. Complete 10 repetitions on each side.
Zapisać się
Zarejestruj się już teraz, aby skorzystać z bezpłatnego okresu próbnego!
Zacznij korzystać z Rehab My Patient już dziś i zrewolucjonizuj proces przepisywania ćwiczeń, aby zapewnić sobie skuteczną rehabilitację.
Rozpocznij 14-dniowy bezpłatny okres próbny