
General information
The extensor digitorum longus is a pennate muscle located in the lower anterior portion of the leg, responsible for extension of the toes and dorsiflexion of the ankle.
Literal meaning
The literal meaning of extensor digitorum longus is “long toe extender”, which is an apt description of its function.
Interesting information
The extensor digitorum longus is one of three muscles involved in dorsiflexion of the foot, which means pulling the toes upwards towards the ankle.
The extensor digitorum longus is commonly used in actions such as walking upstairs. Much like the equivalent tendons in the hand, the extensor digitorum longus makes extensor hoods on the dorsal region of the proximal phalanges of the foot that are joined by the tendons of the lumbricals and extensor digitorum brevis.
Origin
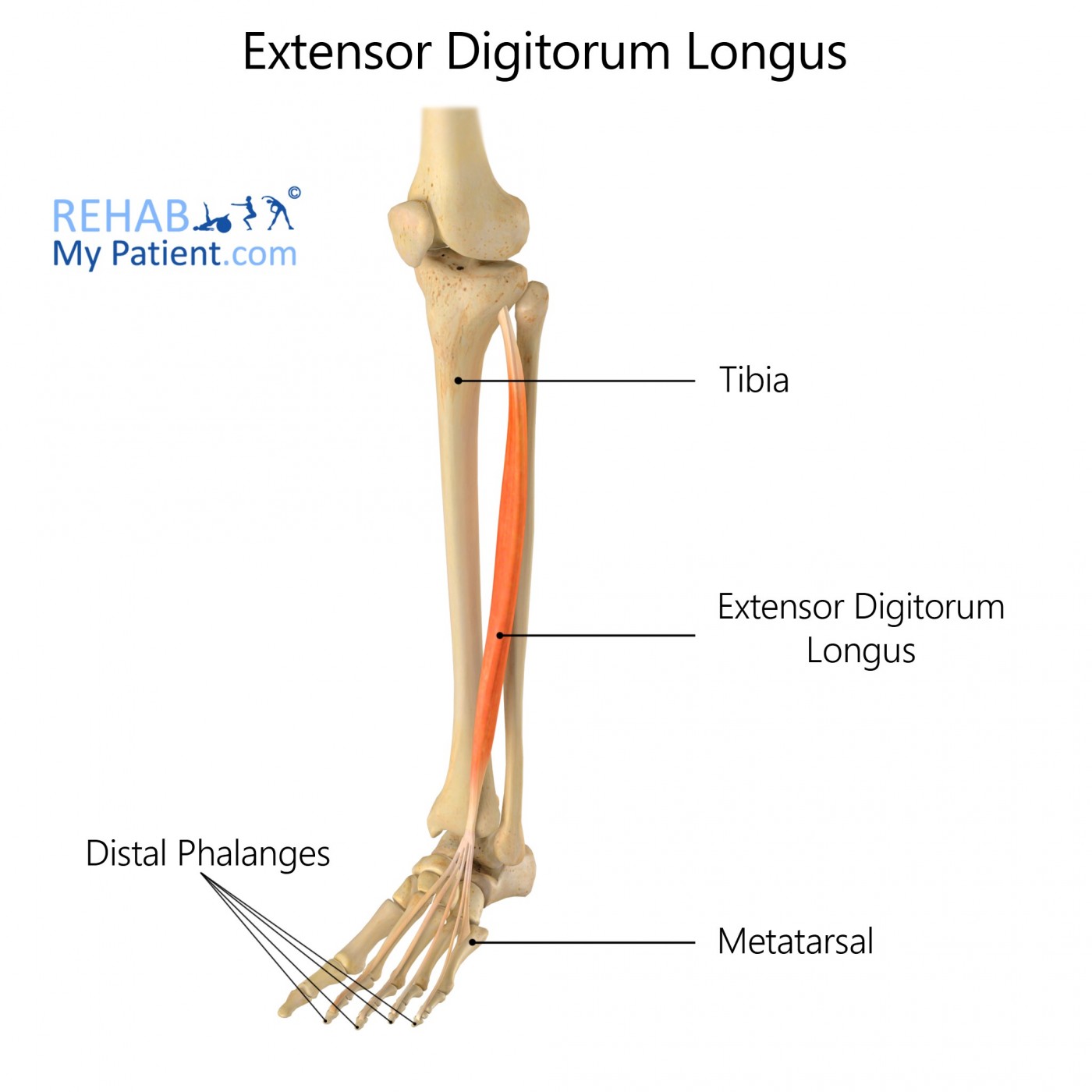
The anterior lateral tibial condyle, anterior shaft of fibula and superior ¾ of the interosseous membrane.
Insertion
The dorsal surface, and middle and distal phalanges of lateral four digits.
Function
The function of the extensor digitorum longus is to extend the toes and dorsiflex the ankle.
Nerve supply
Deep fibular nerve.
Blood supply
Blood is supplied to the extensor digitorum longus via the anterior tibial artery.
Relevant research
A 1994 study by the Department of Neurology at the University of Umeå, Sweden demonstrated that the extensor digitorum longus muscle contains a consistently higher proportion of type 1 fibers in the distal region of the muscle compared to the proximal region. The concentration of type 1 fibers was also shown to be significantly higher in the extensor digitorum longus than in the tibialis anterior.
Lexell, Jarvis, et al., Fibre type composition of rabbit tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscles, J Anat. 1994 Aug;185 ( Pt 1):95-101.
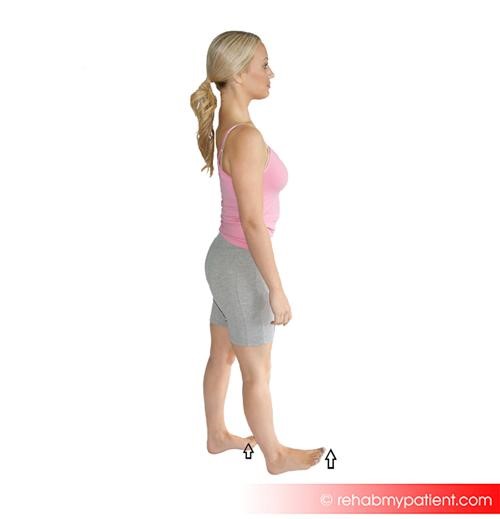
Extensor digitorum longus exercises
Simply walking on the heels is a simple and effective way of exercising the extensor digitorum longus. Do this for 2 minutes every day.

Aside from walking on the heels, ankle dorsiflexion is an often neglected way of exercising the muscles of the lower leg and foot, and can provide a surprising amount of relief to pain and tension in the region.
Dorsiflexion is also an effective method of increasing the strength of muscles such as the extensor digitorum longus to reduce the likelihood of future pain and inflammation.
The following dorsiflexion protocol may be effective in strengthening the muscles of the foot and ankle and providing some release of fascial tension in the extensor digitorum longus:
- Sit on a chair with your foot flat on the ground;
- Lift your toes and front of your foot off the ground and pull them up towards your knee with the heel still touching the ground;
- Lift your toes and forefoot as high as possible and squeeze the muscles of the foot for a two-second count; and
- Return to the starting position.
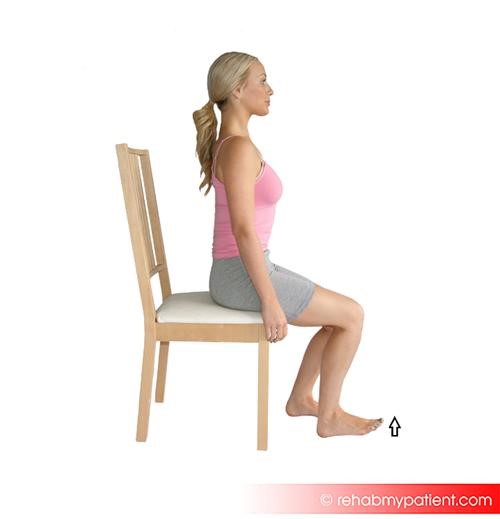

Perform this protocol with one foot at a time and complete 10 repetitions for each foot, repeating the protocol a total of 2-3 times in each session.
Reference
Jarmey (2008), The Concise Book of Muscles, Revised Edition, pg. 173, North Atlantic Books
Zapisać się
Zarejestruj się już teraz, aby skorzystać z bezpłatnego okresu próbnego!
Zacznij korzystać z Rehab My Patient już dziś i zrewolucjonizuj proces przepisywania ćwiczeń, aby zapewnić sobie skuteczną rehabilitację.
Rozpocznij 14-dniowy bezpłatny okres próbny