Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
Opublikowano dnia 23rd Jul 2020 / Opublikowano w: Nadgarstek

General information
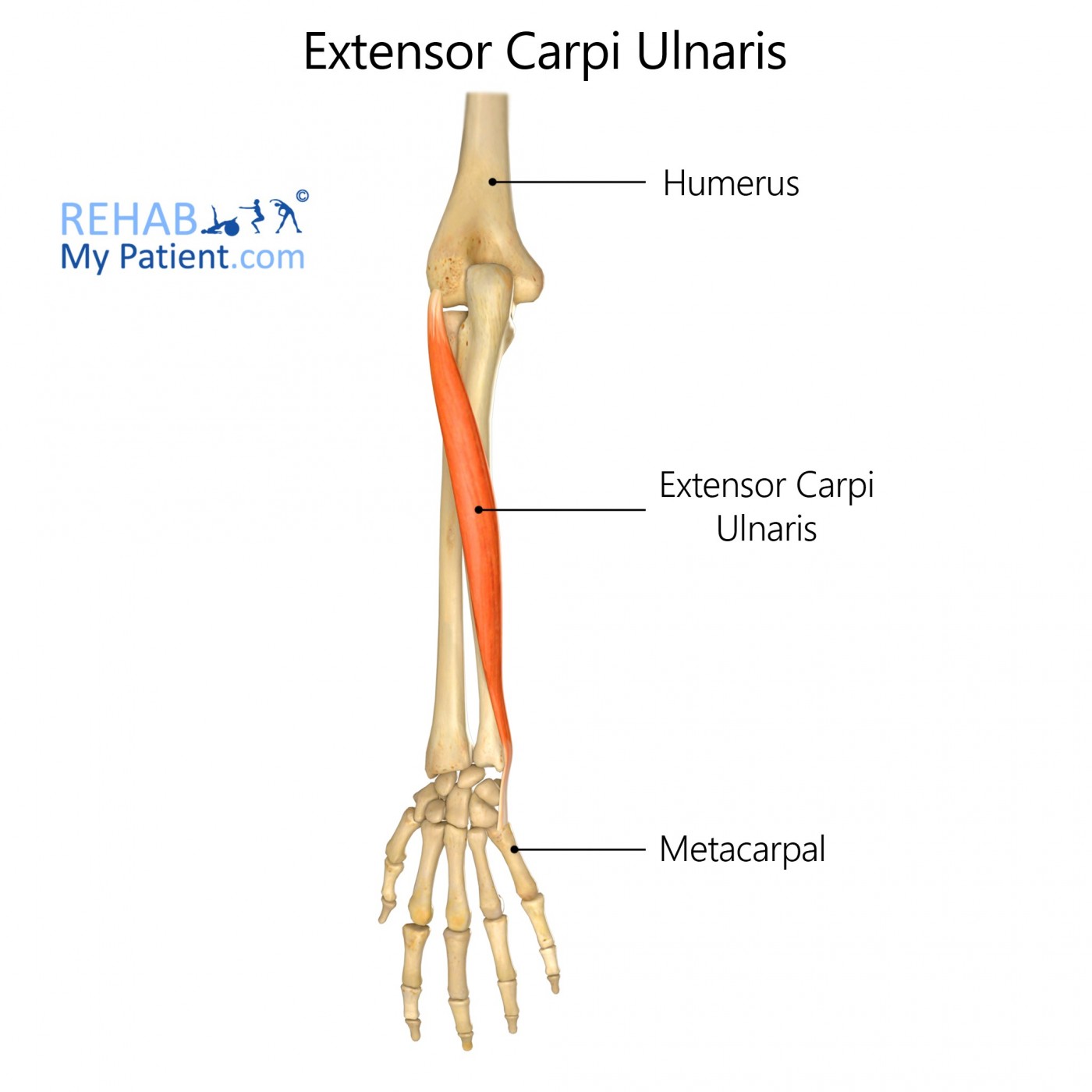
The extensor carpi ulnaris is a skeletal wrist muscle situated on the ulnar or the posterior side of the forearm.
Literal meaning
Muscle on the ulnar side which extends the wrist.
Interesting information
This muscle is the most superficial (the one closest to the skin) of all the forearm muscles. It helps to bend the wrist backwards and also to angle the hand inwards towards the little finger. An everyday activity using this muscle is accelerating a motorbike.
Tennis elbow is a common injury associated with this muscle. It occurs in people whose activities involve repetitive arm, elbow and wrist movements. Tendonitis can also occur with the extensor carpi ulnaris tendon. Symptoms include redness, tenderness or inflammation of the side of the wrist. Pain worsens when the wrist is squeezed like when shaking the hand. Sports like golf, tennis, weightlifting, and bowling can all cause injury to this muscle.
After initial RICE (rest, ice, compression and elevation) treatment and medicines if necessary, stretches and strengthening exercises may be done under supervision. Use of a brace or splint might be advisable depending on the severity. In extreme cases, surgery might be required. Proper warm-up before any sporting activity is essential in preventing injury.
Origin
Lateral epicondyle of humerus and the posterior border of ulna.
Insertion
Medial side of base of the fifth metacarpal bone.
Function
Extension and adduction (ulnar deviation) of the wrist
Nerve supply
Deep branch of the radial nerve (C7 and C8)
Blood supply
Posterior interosseous of the ulnar artery
Relevant research
Recent research shows that tenodesis of the extensor carpi ulnaris can help optimize grip strength and help in more ergonomic use of the hand in patients with cervical spinal cord injury or tetraplegia. Grip strength was shown to be doubled when grip reconstruction was done with tenodesis of this muscle. Tenodesis also may help prevent shoulder pain, common in patients having this condition.
Reinholdt C, Fridén J (2013). “Rebalancing the tetraplegic wrist using extensor carpi ulnaris-tenodesis”. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2013 Jan; 38(1):22-8.
A case study of tennis players having extensor carpi ulnaris injuries has identified three clinical patterns of pathology – acute instability of the muscle, tendinopathy and muscle rupture.
B Montalvan, J Parier, J L Brasseur, D L Viet, J L Drape (2006). “Extensor carpi ulnaris injuries in tennis players: a study of 28 cases”. Br J Sports Med 2006; 40:424-429
Extensor carpi ulnaris exercises
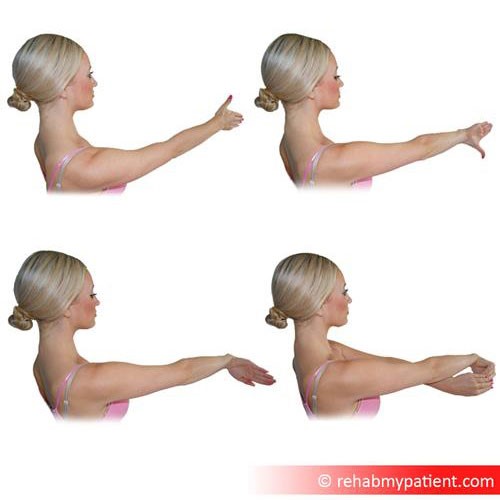
The Tennis Elbow Stretch is very effective in preventing and treating extensor carpi ulnaris injuries. Hold your arm out in front of you, straighten it, rotate your arm inwards (so your elbow crease faces down towards the floor) and bend your wrist back. Hold this position to create a stretch. This exercise stretches the forearm extensor muscles, and can help with tennis elbow pain and other repetitive strain injuries.

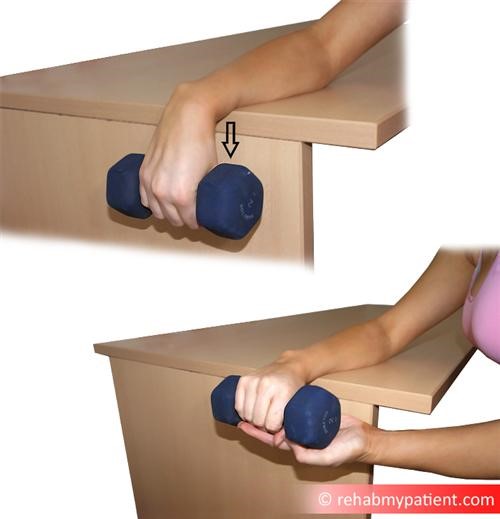
The eccentric tennis elbow strengthening exercise is one of the most effective exercises for tennis elbow pain relief. Rest your arm on a table with your palm facing down, and hold a 1-2kg dumbbell. Lift your hand upwards using your other hand, and then with a controlled movement let the weight pull your hand back down. At the bottom, repeat by lifting your own hand upwards again, and then letting the weight pull your hand back down. Eccentric exercises are a very effective way to rehabilitate the wrist, forearm and elbow, and this can be especially useful for tennis elbow.

Zapisać się
Zarejestruj się już teraz, aby skorzystać z bezpłatnego okresu próbnego!
Zacznij korzystać z Rehab My Patient już dziś i zrewolucjonizuj proces przepisywania ćwiczeń, aby zapewnić sobie skuteczną rehabilitację.
Rozpocznij 14-dniowy bezpłatny okres próbny